We are nearly all the descendants of immigrants, those hearty people who risked everything to start again in a new land. Their bravery and fortitude made our country what it is today, made each of us what we are today.
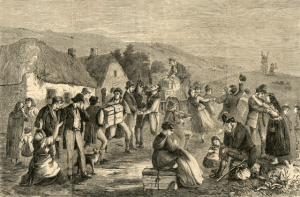 To emigrate in the Seventeenth or Eighteenth Century was to leap by faith alone into the unknown, leaving behind home and family, familiar neighborhoods, routines well established, even loved ones they never wished to leave behind. All to begin again from scratch with little more than a few precious dollars and enormous stores of energy and faith.
To emigrate in the Seventeenth or Eighteenth Century was to leap by faith alone into the unknown, leaving behind home and family, familiar neighborhoods, routines well established, even loved ones they never wished to leave behind. All to begin again from scratch with little more than a few precious dollars and enormous stores of energy and faith.
Most of us fortunate enough to have been born in America will never know the immigrant experience. We’ll never know those forces of poverty, oppression, or persecution so strong that  they drive emigrants to leave their homes and venture into the unknown. We’ll never know their particular kind of hope and fear mixed with regret and relief, the concoction of emotions that has driven immigrants to our land for nearly four hundred years, and continues to drive them today.
they drive emigrants to leave their homes and venture into the unknown. We’ll never know their particular kind of hope and fear mixed with regret and relief, the concoction of emotions that has driven immigrants to our land for nearly four hundred years, and continues to drive them today.
Hope, fear, regret, and relief. What recipe is this? It is when we leave anything once loved behind in order to better our lives. A lover, a spouse, a job, a home, a town, a country. We hope for better lives, but fear the unknown. We regret that our lives didn’t work out as planned, but feel relief at being free of untenable circumstances. We feel nothing as simple as a single emotion, but a mixture so foreign that we can’t put our fingers on it. And so the emotions churn about and we describe it physically, as feeling numb, or having a reeling head or a pounding heart.
For our Seventeenth and Eighteenth Century ancestors who left their fertile Rhine River Valley homeland in Germany to seek better life in America,  the need to leave was acute. Their country had been the finest in Europe, a land of noble heroes and spectacular scenery, of majestic castles and cathedrals and prosperous farms and orchards. But forces conspired to make life difficult for our ancestors there.
the need to leave was acute. Their country had been the finest in Europe, a land of noble heroes and spectacular scenery, of majestic castles and cathedrals and prosperous farms and orchards. But forces conspired to make life difficult for our ancestors there.
Traditional inheritance practices in Germany meant that land was divided equally between all children, which meant that farms were made increasingly smaller, and land hunger drove the people to search farther afield for suitable property. More important, Germany was torn by nearly ceaseless war, its once mighty empire in now in fragments, its people desperate and hungry.
The Holy Roman Empire of Germany during the Middle Ages was the wealthiest and most powerful in all Europe. Art and science flourished there. Johannes Gutenberg invented the movable type, which made possible the Enlightenment and the spread of knowledge throughout the civilized world. Germany’s prosperous farmers and skilled craftsmen were hailed as the finest in all Europe.
Then in the early 1500s Martin Luther translated the Bible into German and gave his people not only direct access to the word of God, but the language of literature and poetry. Luther didn’t stop there, though. He went on to publicly question the very tenants of the Catholic Church, leading others to do the same and sparking one of the greatest revolutions of all time, the Protestant Reformation, and leading the way to the Age of Enlightenment.
But the road to Enlightenment was full of terror and violence. And thus was ushered in one of the most destructive and longest wars in European history. The Holy Roman Empire was fragmenting. War after war raged through the land. The Thirty Years War, the Seven Years War, the War of the Grand Alliance, the War of the Spanish Succession.
One after another they crashed like tidal waves against the people, wreaking more destruction each time until carnage covered the land and  the countryside and its people were in ruin. Religious hatred and political divisions pitted Catholic against Protestant, Hapsburg against Ottoman, north against south, prince against prince, and in their armies, peasant and farmer against peasant and farmer. The devastation was enormous, the taxes oppressive as local leaders sought more and more money to wage war.
the countryside and its people were in ruin. Religious hatred and political divisions pitted Catholic against Protestant, Hapsburg against Ottoman, north against south, prince against prince, and in their armies, peasant and farmer against peasant and farmer. The devastation was enormous, the taxes oppressive as local leaders sought more and more money to wage war.
The country’s population was ravaged, falling from thirty million to twelve million as the Holy Roman Empire fought for its very existence against the rise of Protestantism. As in any war, the common people suffered disproportionately. Some fled. Many died.
Unpaid armies and bands of mercenaries roamed the countryside pillaging and plundering, villages left burning and their people dead or without sustenance. And then the winter of 1708 came, the coldest in 100 years. Birds, it was said, froze in mid-air, men mid-step. Farms and their farmers perished in the cold, and the people cried, “Enough!” Those who could, left.
 Many fled to Switzerland or the Alsace region of France. After the end of hostilities some went home, some stayed, but many came to America, mostly to Pennsylvania. A generation before, William Penn visited Germany to spread the word that Pennsylvania would welcome them.
Many fled to Switzerland or the Alsace region of France. After the end of hostilities some went home, some stayed, but many came to America, mostly to Pennsylvania. A generation before, William Penn visited Germany to spread the word that Pennsylvania would welcome them.
Some were old enough to remember the handbills passed out by his agents throughout the country proclaiming a land of milk and honey; a place where the climate was temperate, the fertile soil nearly free, kings and princes unknown, and religious and political tolerance the cornerstones of society. A place where Germans could prosper and thrive, free at last. If only they could get there.
And so our ancestors pleaded their case to England’s Queen Anne, saying,
“We, the poor, distressed Palatines, whose utter ruin was occasioned by the merciless cruelty of a bloody enemy whose prevailing power, some years past, like a torrent, rushed into our country and overwhelmed us at once; and being not content with money and food necessary for their occasions, not only dispossessed us of all support, but inhumanly burnt our houses to the ground, whereby being deprived of all shelter, we were turned into open fields, there with our families to seek what shelter we could find, were obliged to make the earth our repository for rest and the clouds the canopy for covering.”
The sympathetic queen thus invited the beleaguered Protestant Germans to sail to America on English ships,  offering them passage and land in exchange for bonded labor.
offering them passage and land in exchange for bonded labor.
By the thousands, they packed their meager belongings and headed for the promised land. From May to November of 1709 nearly thirteen thousand passengers left their desolate homeland and sailed the Rhine to Rotterdam, and on to England. By June there were one thousand immigrants passing through Rotterdam every week.
Of those, there were 2,257 Catholics who were sent back. The enmity between the two was far from over. One historical account written in 1897 quotes a contemporary diarist who wrote, “Thursday, 29 September [1709]. The Popish Palatines who came hither, were ordered to go home, having passports for the same.”  Queen Anne knew exactly who she wanted to populate her colonies. She was designing her ideal New World.
Queen Anne knew exactly who she wanted to populate her colonies. She was designing her ideal New World.
After arriving in England, from there our ancestors traveled on to Canada, Australia, Ireland, or America. Once in America the Protestant Germans who answered Queen Anne’s offer were required to pay off their price of passage by working in camps set up for that purpose along the Hudson River.
After that tour of duty, which typically lasted five to seven years, they were finally free. Free to practice their religion. Free to find and homestead land. Free to join in building a new country that was free to all.
Many of the immigrants made their way to William Penn’s land, which had been given to that quirky Quaker by England’s Charles II in repayment of a debt to 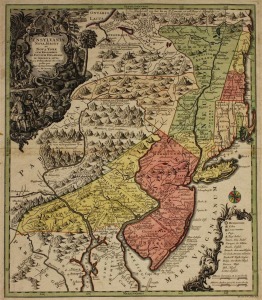 Penn’s father, one of the largest land grants awarded an individual in all history. Penn wished to name the land Sylvania for its vast forests of trees, but the king wanted to name it in honor of Penn’s father. They compromised, and the land became known as Pennsylvania.
Penn’s father, one of the largest land grants awarded an individual in all history. Penn wished to name the land Sylvania for its vast forests of trees, but the king wanted to name it in honor of Penn’s father. They compromised, and the land became known as Pennsylvania.
Lutherans, Reformed, Swiss Mennonites, Baptist Dunkers, Moravians, Quakers, and Amish all flooded into Pennsylvania’s wilder regions. A second wave of immigrants began in 1727, and from then to 1775, around 65,000 Germans landed in Philadelphia and settled in Pennsylvania.
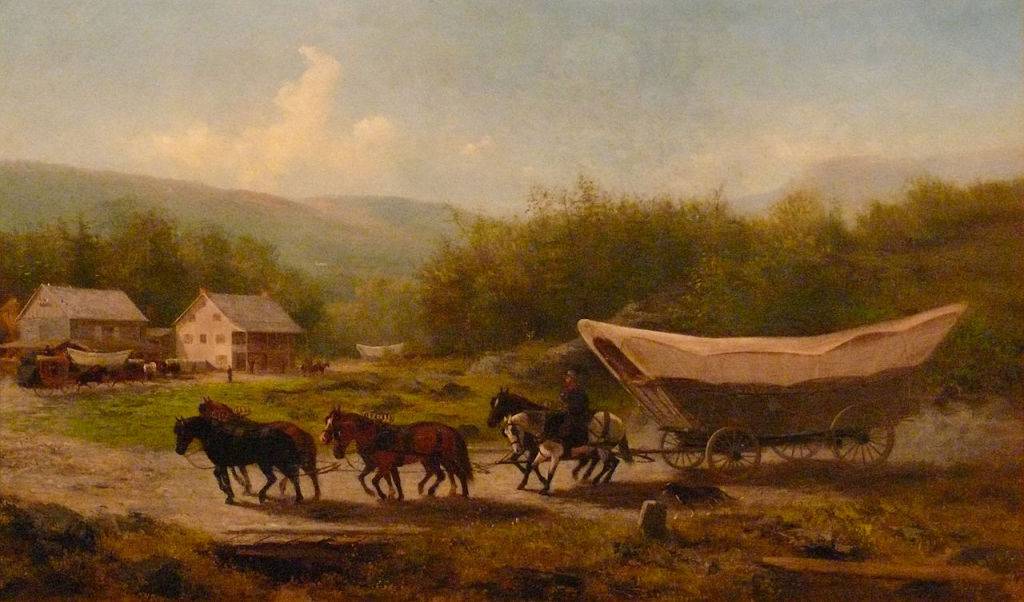
These are our ancestors, the ones who survived war and religious persecution to find their way to America and once here, to build strong frontier families that made their way without the aid of anyone excepting their nearest neighbors, who were also a hearty stock of immigrants. They cut their homes from the forest and built their farms with blood and sweat. They survived and thrived and raised their families well, which led, in the end, to you and me.
So when you think on your German ancestors, think of the historical times in which they lived, the history-making events they endured and helped to shape, and the hope, fear, regret, and relief they felt to the depths of their being in coming to America. We can be proud of such character and strength that brought them here. And remember, those genes reside in us, too.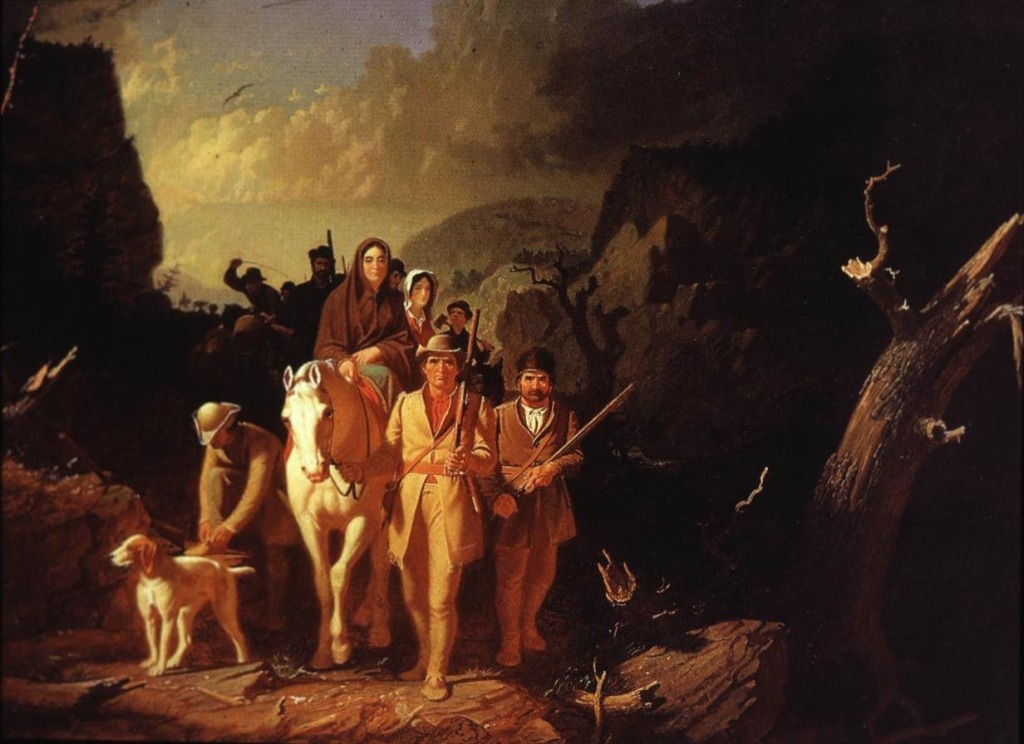









 Of the Blue Ridge, he wrote:
Of the Blue Ridge, he wrote: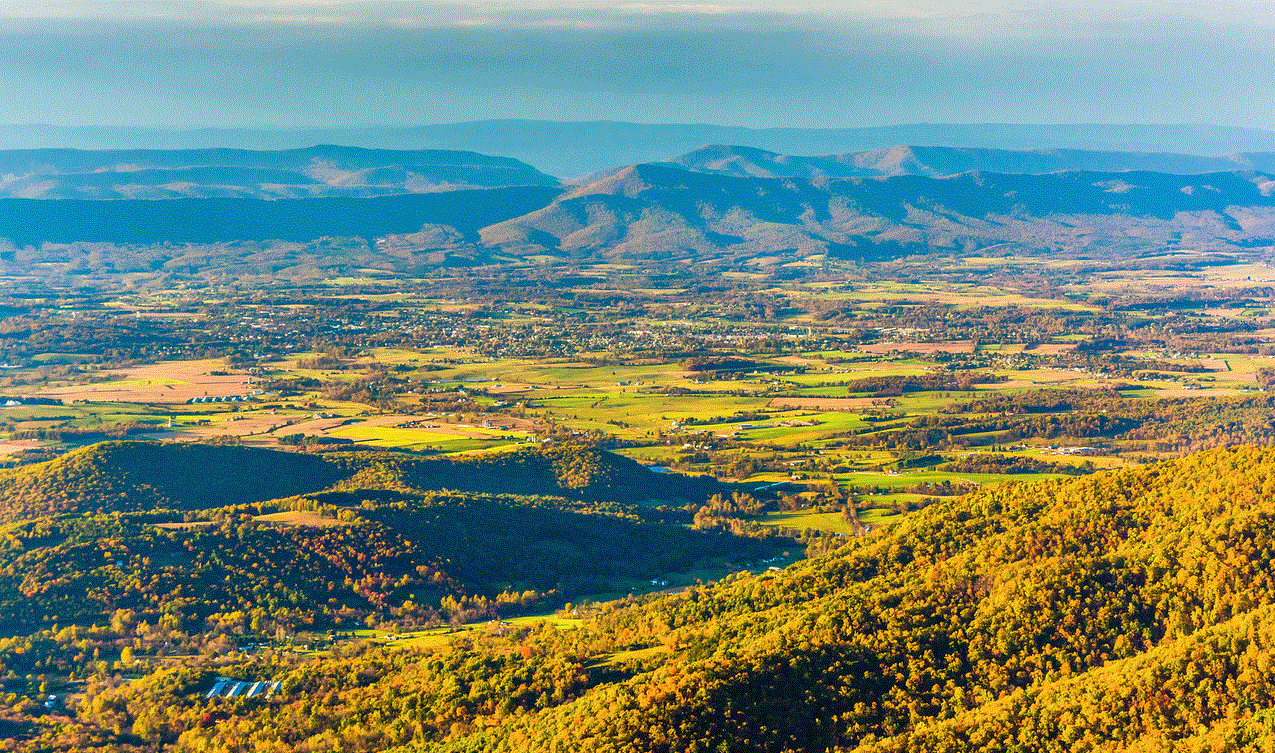 And of Shenandoahans, he wrote:
And of Shenandoahans, he wrote: I couldn’t agree more.
I couldn’t agree more.

 Captive-taking by Native Americans was surprisingly common in Colonial times.
Captive-taking by Native Americans was surprisingly common in Colonial times. nd journalists who sensationalized stories of captor brutality that today’s academics call “capture narratives.”
nd journalists who sensationalized stories of captor brutality that today’s academics call “capture narratives.” Once in the villages, the captives were given Indian clothes, taught Indian songs and dances, and welcomed as family members into specifically appointed adoptive families.
Once in the villages, the captives were given Indian clothes, taught Indian songs and dances, and welcomed as family members into specifically appointed adoptive families.

 John Boyd and Nancy Urie thought they found it in the unbroken wilderness of Pennsylvania’s Cumberland Valley.
John Boyd and Nancy Urie thought they found it in the unbroken wilderness of Pennsylvania’s Cumberland Valley. On February 10, 1756, John and his oldest son, William, started out for Stewart’s to buy a web of cloth.
On February 10, 1756, John and his oldest son, William, started out for Stewart’s to buy a web of cloth. Their two sisters, Sallie and Rhoda, ten and seven, stayed inside with their mother and little brother.
Their two sisters, Sallie and Rhoda, ten and seven, stayed inside with their mother and little brother. He was concentrating so hard, in fact, that he didn’t hear the Iroquois Indian who had walked right up to him.
He was concentrating so hard, in fact, that he didn’t hear the Iroquois Indian who had walked right up to him. The Natives instructed the children to run.
The Natives instructed the children to run. The children were traumatized. But they did as their captors told them, running on the trail, always running, and staying silent.
The children were traumatized. But they did as their captors told them, running on the trail, always running, and staying silent. You would think that a captor brutal enough to slaughter a babe before his mother and a mother before her children could not show humanity.
You would think that a captor brutal enough to slaughter a babe before his mother and a mother before her children could not show humanity. hey learned lessons of the forest and the stars and the animals. They became what people of the day called white Indians.
hey learned lessons of the forest and the stars and the animals. They became what people of the day called white Indians.

 Of course, they probably weren’t odd for the time, and that’s where it helps to put on your best Sherlock Holmes deerstalker hat and play Ancestral Name Detective.
Of course, they probably weren’t odd for the time, and that’s where it helps to put on your best Sherlock Holmes deerstalker hat and play Ancestral Name Detective. It’s no trick at all to know that my ancestors, Silence Brown, Delight Kent, Mindwell Osborne, Temperance Stewart, and Thankful Clapp were all named in the trendy Puritan practice of choosing virtues as children’s names.
It’s no trick at all to know that my ancestors, Silence Brown, Delight Kent, Mindwell Osborne, Temperance Stewart, and Thankful Clapp were all named in the trendy Puritan practice of choosing virtues as children’s names.


 Then someone else started in on adjectives, like Short, Little, Red, or White.
Then someone else started in on adjectives, like Short, Little, Red, or White.